- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2024-01-11 06:21.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
Microsoft Access is a database creation program that allows anyone to create and manage databases. This program is suitable for small projects to large businesses, and operates very visually. This makes it excellent for data entry, as you don't have to work with tables or worksheets. Check out the first steps below to get started with getting the most out of Microsoft Access.
Step
Part 1 of 6: Creating a New Database
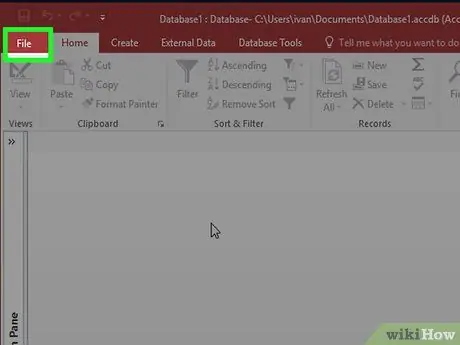
Step 1. Click the File tab and select "New"
A database is a place where your data is stored in various forms. You can choose to create an empty database, or choose from an existing template.
- An empty database is the standard Access database, and is recommended for local use. Creating a local database will include a table.
- Web databases are designed to be compatible with Access web devices. Creating a web database will include a table.
- Templates are databases that have been designed for various uses. Choose a template if you don't want to spend time designing the database.
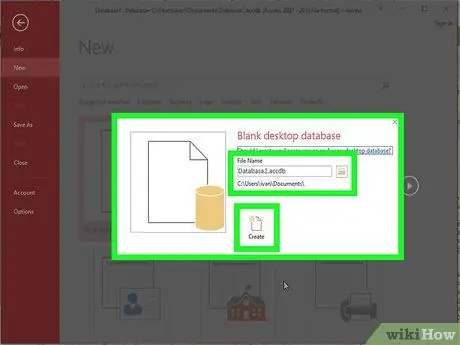
Step 2. Name the database
Once you have selected the database type, give it a name that reflects its contents. This is especially useful if you will be working with many different databases. Enter the name of your database in the "File Name" box. Select "Create" to create a new database file.
Part 2 of 6: Adding Data to Database
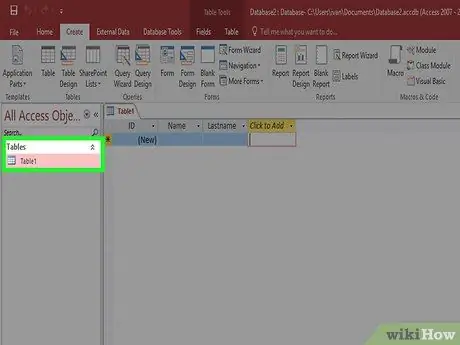
Step 1. Determine the best structure for your data
If you are creating an empty database, you will need to think about how to organize your data and add proper data structures. There are various ways to format and interact with your data in Access:
- Tables - Tables are the primary way of storing data in your database. Tables can be compared to worksheets in Excel: data is organized in columns and tables. Therefore, importing data from Excel and other number processing programs is an easy process.
- Forms - Forms are a way of adding data to your database. Although you can add data to the database directly in tables, using forms will speed up visual entry of data.
- Reports - Reports are useful for summarizing and displaying data from your database. Reports are used to analyze data and answer specific questions, such as how much profit was made, or where the most customers are. Reports are designed to be printed.
- Query - Query is the way you receive and sort data. You can use it to display specific entries from various tables. You can also use queries to add and update data.
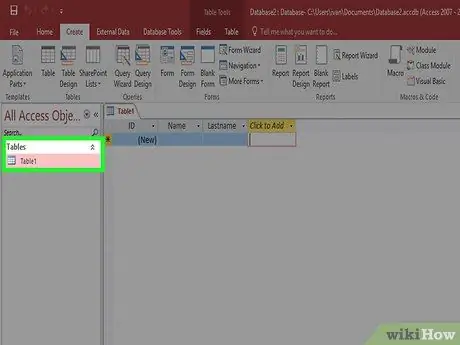
Step 2. Create your first table
If you start an empty database, you will start with an empty table. You can start entering data in this table, either manually or by copying it from another source.
- Each piece of data must be stored in its own column (field), while the data must be placed in its own row. For example, each customer's data is stored in a row, while the available fields are different information about that consumer (first name, last name, email address, etc.)
- You can name the column labels to make it easier for you to know the name of each field. Double-click the column header to rename it.
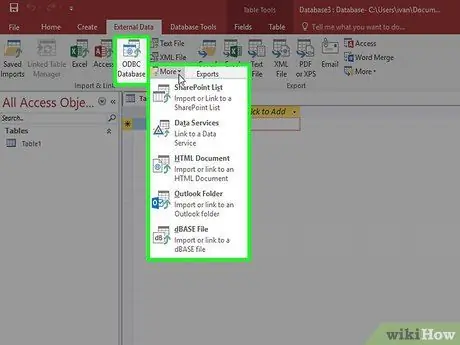
Step 3. Import data from other sources
If you want to import from a supported file or location, you can set Access to accept the information and add it to your database. This is useful for receiving data from web servers or other shared sources.
- Click the External Data tab
- Select the type of file you want to import. In the "Import and Link" section, you will see several options for data types. You can click More to see more options. ODBC stands for Open Database Connectivity, and includes databases such as SQL.
- Browse data locations. If the data is on the server, you need to enter the server address.
- In the next window, select "Specify how and where you want to store the data in the current database". Select "OK". Follow the steps to import your data.
Step 4. Add another table
You will want to store different records in different databases. This will make your database run smoothly. For example, you might have a customer information table and another table for ordering information. You can then link the customer information table to the order information table.
In the "Create" section of the Home tab, click the "Table" button. A new table will appear in your database. You can enter information in the same way as the first table
Part 3 of 6: Managing Relationships Between Tables
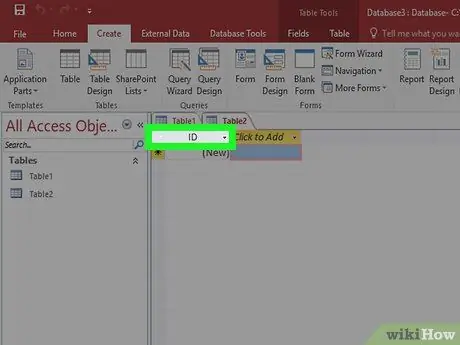
Step 1. Understand how locks work
Each table will have a unique primary key for each entry. Initially, Access creates an ID column whose number increases with each entry. This column will act as the "primary key". Tables can also have "foreign key" fields, which are linked fields from other tables in the database. The linked fields will have the same data.
- For example, in the Orders table, you might have a Customer ID field to record what the customer ordered. You can create a relationship for that field with the ID field in the Customers table.
- Using relationships between tables will help with the consistency, efficiency, and ease of access of your data.
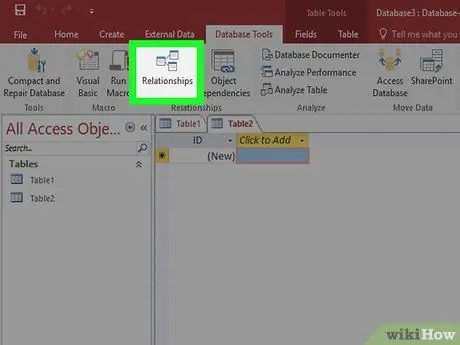
Step 2. Click the Database Tools tab, then click the Relationships button in the Relationships section
This will open a new window with a preview of all the tables in the database. Each field will be displayed under the name of each table.
You must create a field for "foreign key" before creating a relationship. For example, if you want to use Customer ID in the Orders table, create a field named Customer in the table and leave the field blank. Make sure the format is the same as the field you are linking to (eg numbers)
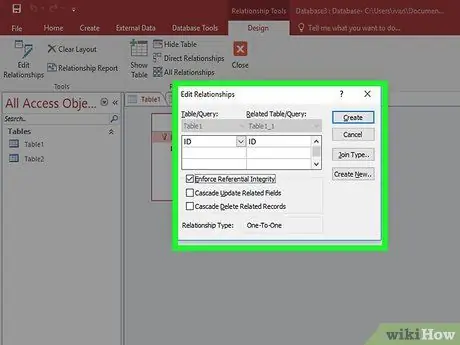
Step 3. Drag the field you want to use as a foreign key to the field you created for the foreign key
Click Create in the window that appears to set the relationship between the fields. A line will appear between the two tables connecting the two fields.
Check the "Enforce Referential Integrity" checkbox when creating a relationship. This means, if the data is changed in one field, the data in other fields will also change. This will make your data more accurate
Part 4 of 6: Creating a Query
Step 1. Understand the role of queries
Queries are actions that allow you to quickly view, add, and edit data in a database. There are many types of queries, ranging from simple searches to creating new tables based on existing data. Queries are important in report generation.
Queries are divided into two main types: Select and Action. The first query pulls data from the table and can compute it, while the second can add, edit, and delete data from the table
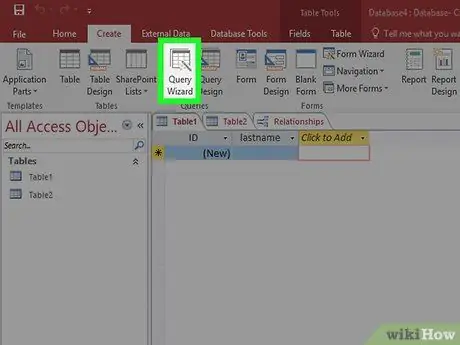
Step 2. Use the Query Wizard to create a basic Select query
If you want to use a basic Select query, use the Query Wizard to guide you through the steps. You can access the Query Wizard from the Create tab. This allows you to display specific fields from a table.
Creating a Select Query with Criteria
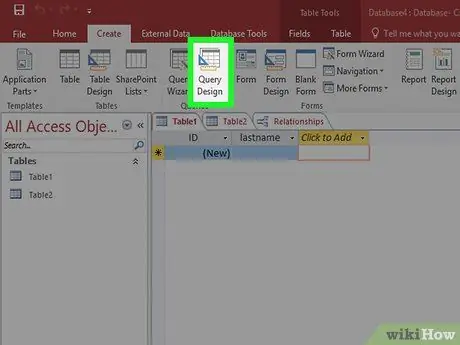
Step 1. Open Query Design
You can use criteria to minimize your Select query and display only the information you need. To get started, click the Create tab, and select Query Design.
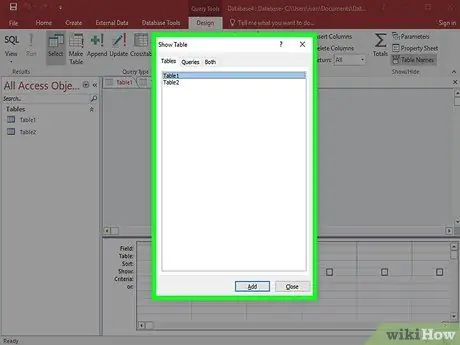
Step 2. Select your table
The Show Table box will open. Double-click the table you want to use, and click Close.
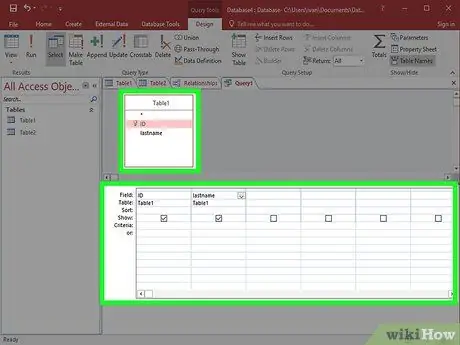
Step 3. Add the fields to which the data will be extracted
Double-click each field in the table that you want to add to the Query. The field will be added to the Design list.
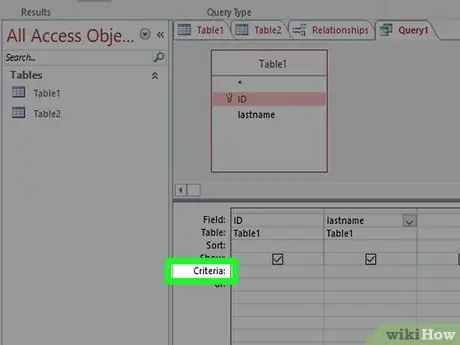
Step 4. Add criteria
You can use different types of criteria, such as text or functions. For example, if you want to display a price higher than $50 from the Price field, enter
=50
on the criteria. If you only want to show customers from the UK, enter
UK
in the Criteria box.
You can use various criteria in each query
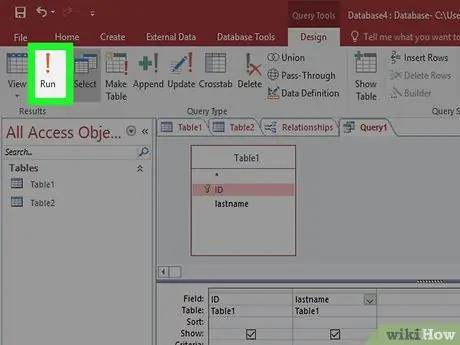
Step 5. Click "Run" to see the result
This button is on the Design tab. The results of your query will be displayed in the window. Press Ctrl+S to save the query..
Creating a Select Query with Parameters
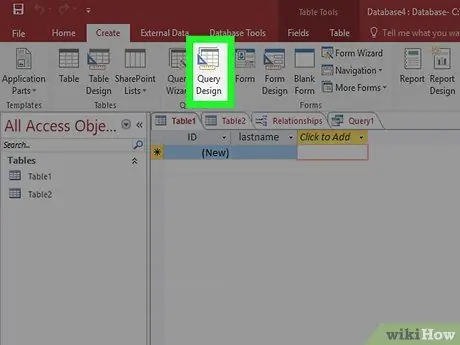
Step 1. Open Query Design
Query with parameters allows you to set what data you want to receive each time you run a query. For example, if you have a database of customers from different cities, you can use a query with parameters to ask which city you want to display data for.
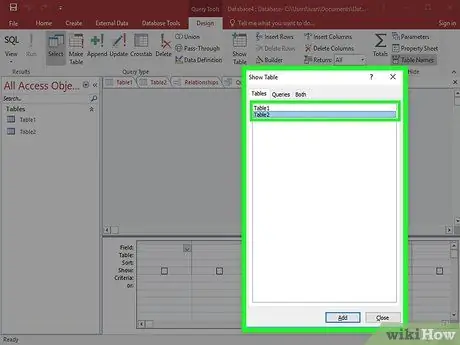
Step 2. Create a Select query and define the table
Add the fields you want to retrieve data for in the query by double clicking on the table preview.
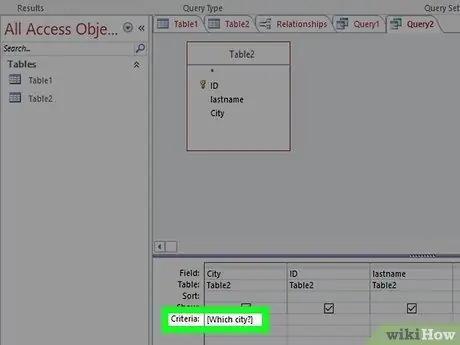
Step 3. Add parameters in the Criteria section
Parameters are marked with "" characters around them. The text in brackets will be displayed on the query that appears when the query is executed. For example, to request city input, click the Criteria cell for the City field, and enter
[Which city?]
You can end parameters with ? or:, but not with ! or
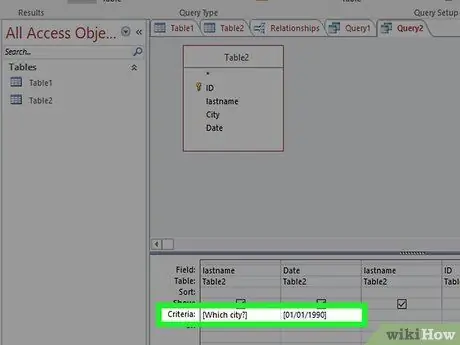
Step 4. Create a query with many parameters
You can use multiple parameters to create custom spacing in your query results. For example, if your preferred field is Date, you can get results between specific dates by typing code>Between[Start Date:] And [End Date:]. You will receive two prompts when you run the query.
Creating a Table Creation Query
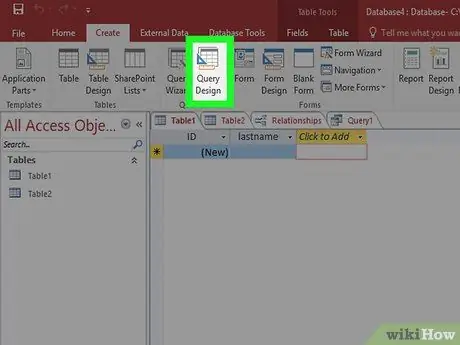
Step 1. Click the Create tab and select Query Design
You can use a query to retrieve specific data from an existing table and create a new table with that data. This is very useful if you want to split a specific part of your database, or create a form for a specific part of the database. You will create a regular Select query first.
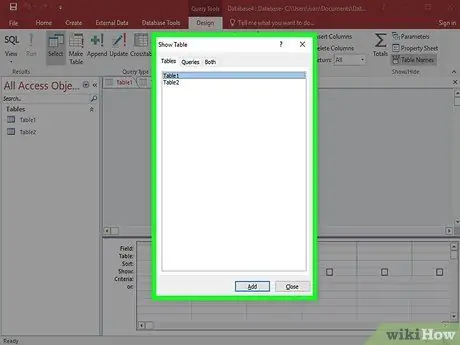
Step 2. Select the table you want to retrieve data from
Double-click the tables. You can select multiple tables at once if necessary.
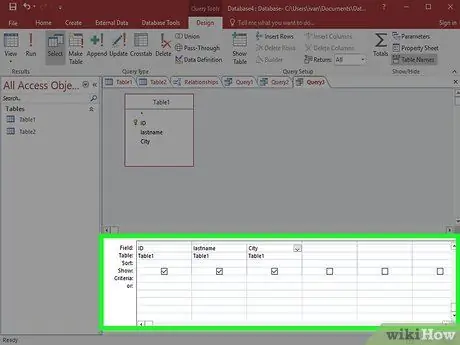
Step 3. Select the field you want to retrieve data from
Double-click each field you want to add from the table preview. This field will be added to your query list.
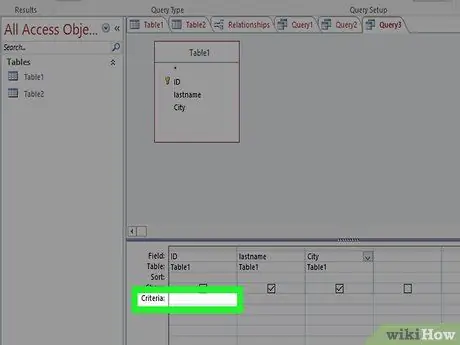
Step 4. Set the criteria
If you want to specify certain data in a field, use the Criteria section to set it. See the section "Creating a Select Query with Criteria" for details.
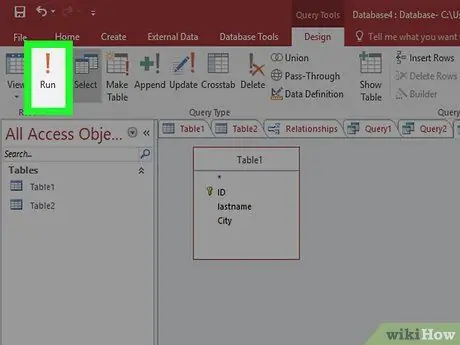
Step 5. Test your query to make sure the results match your needs
Before you create your table, run a query to make sure it retrieves the correct data. Adjust the criteria and fields until you get the right data.
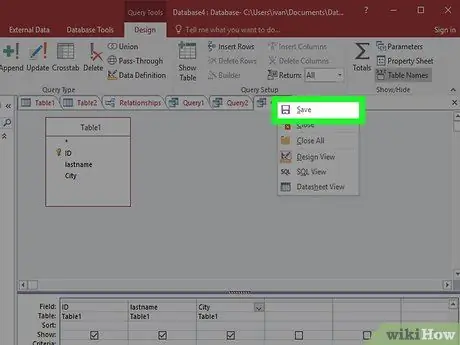
Step 6. Save the query by pressing Ctrl+S
The query will appear in the navigation frame on the left of the screen. Click on the query to select it again and click the Design tab.
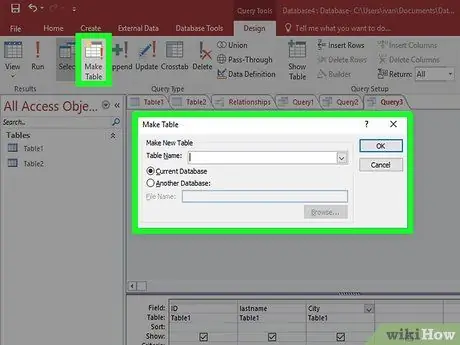
Step 7. Click "Make Table" in the "Query Type" section
A window will appear asking for a new table name. Enter a table name and click OK.
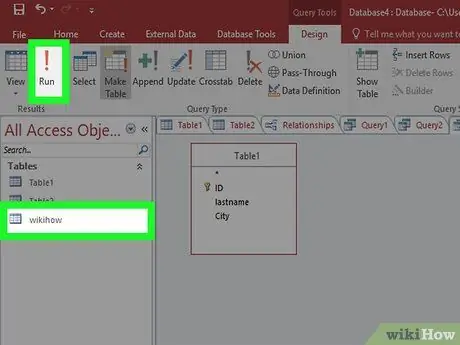
Step 8. Click Run
Your new table will be created based on the query you have built. The table will appear in the navigation frame on the left of the screen.
Creating Append Query
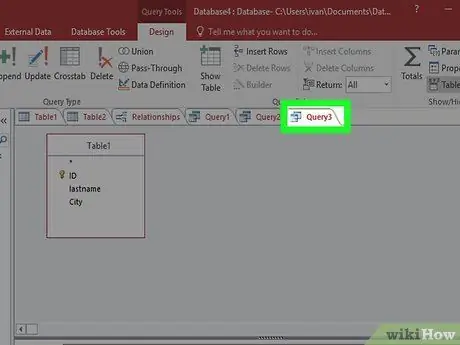
Step 1. Open the Query that was created earlier
You can use an Append query to add data to an existing table from another table. This is useful if you need to add data to a table that you have created through a table creation query.
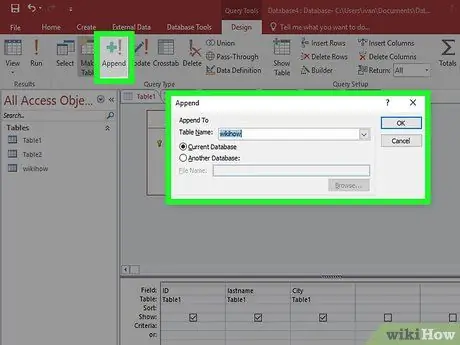
Step 2. Click the Append button on the Design tab
This will open the Append window. Select the table you want to add data to.
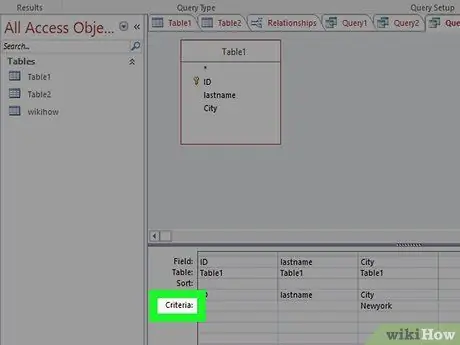
Step 3. Change your query criteria as desired
For example, if you create a table with the criteria "2010" in the "Year" field, change it to the year you want to add, for example "2011".
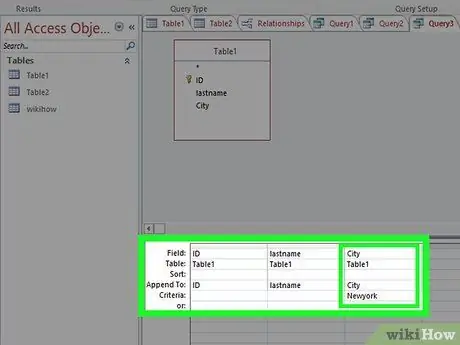
Step 4. Set where you want to add the data
Make sure you set the correct fields for each column you add data to. For example, using the above changes, the data should be added to the Year box in the "Append To" row.
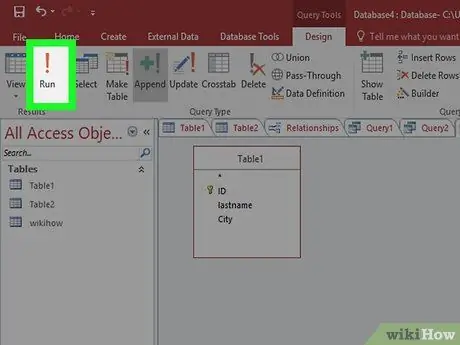
Step 5. Run the query
Click "Run" on the Design tab. The query will be executed and the data will be added to the table. You can then add a table to check if the data was entered correctly.
Part 5 of 6: Creating and Using Forms
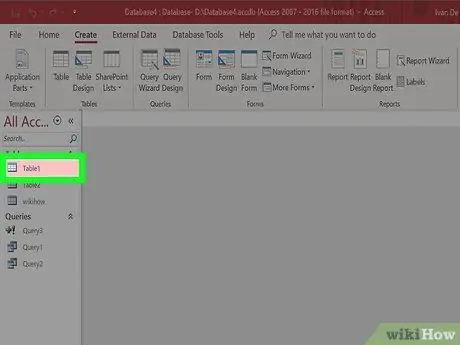
Step 1. Select the table you want to create the form for
Forms allow you to view data in each field and move between entries and create new entries quickly and easily. Forms are very important if you enter data over a long period of time, because many people find it easier to use than tables.
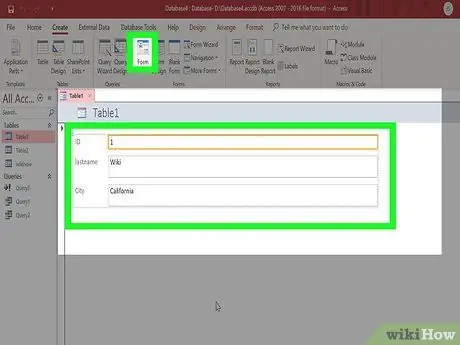
Step 2. Click the Form button on the Create tab
This will create a form based on the fields in the table automatically. Access creates fields of sufficient size, but you can resize and move elements on the form at will.
- If you don't want certain fields to appear on the form, you can right-click and select Delete.
- If your table has a relationship, a row of data will appear below each entry that displays the linked data. This allows you to edit linked data more easily. For example, each salesperson in your database might have customer data linked to their entry.
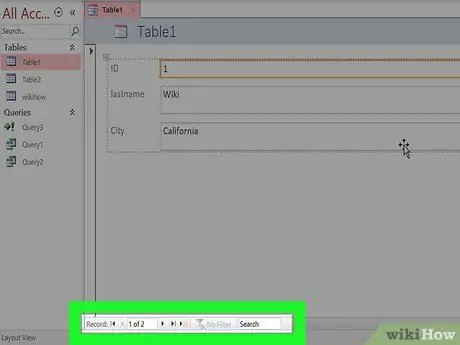
Step 3. Browse to your form
The directional buttons at the bottom are useful for moving between entries. The boxes on the form will be filled with your data as you move between entries. You can use the buttons in the corner to move to the first or last record.
Step 4. Click the Datasheet button to use the table
This button is at the top left, and will allow you to start changing your data content with the form.
Step 5. Change the entries you have made
You can edit the text in the entire box for each entry to change the existing data in the table. Changes made will appear immediately on the table and linked data.
Step 6. Add a new entry
Click the "Add Record" button near the navigation buttons to create a new entry at the end of the line. You can use boxes to enter data in empty boxes in the table. This is an easy way of adding information, instead of using a table view.
Step 7. Save the form when finished
Make sure you save the form by pressing Ctrl + S so you can access it at a later date. The form will appear in the navigation frame on the left of the screen.
Part 6 of 6: Making a Report
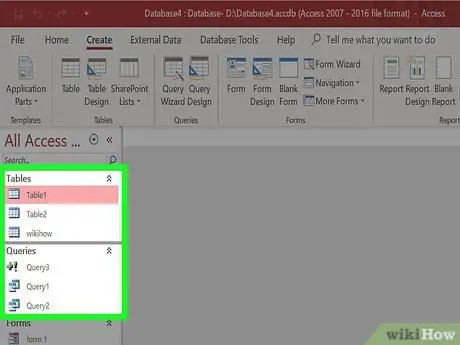
Step 1. Select a table or query
Reports will allow you to display a summary of your data. Reports are often used for payroll and delivery reports, and can be customized for any use. Reports retrieve data from tables or queries that you have created.
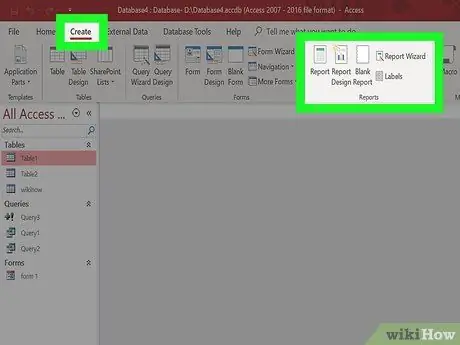
Step 2. Click the Create tab
Select the type of report you want to create. There are several ways of making reports that you can do. Access can generate reports for you automatically, and you can also create custom reports.
- Report - This will generate an automatic report with all the data from your source. There is no grouping of data here, but for small databases this type of report may be suitable for your needs.
- Blank Report - This will create a blank report that you can fill in the data at will. You can choose from the available fields to create a custom report.
- Report Wizard - The report creation wizard will guide you through the report creation process, allowing you to select and group data, and format the data.
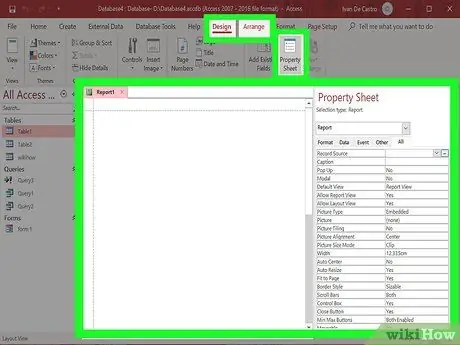
Step 3. Select the data source for your blank report
If you choose to generate a blank report, you must select the data source. First, click the Arrange tab, and select Property Sheet. Or, you can also press Alt+Enter.
Click the down arrow next to Record Source. A list of your tables and queries will appear. Select a table or query and your options will be selected for the report
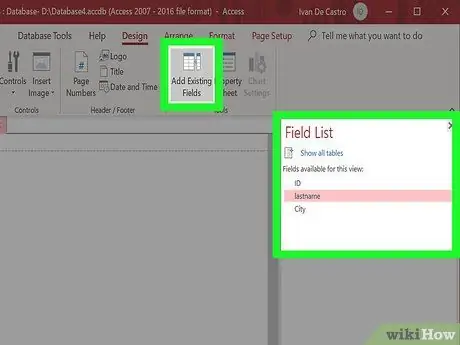
Step 4. Add fields to your report
Once you have the sources, you can add fields to your report. Click the "Format" tab, and click "Add Existing Field". A list of fields will appear on the right.
- Click and drag the fields you want to add to the Design frame. The entry will appear on your report. When you add additional fields, they will be set automatically with the existing fields.
- You can change the size of a field by clicking on its corner and dragging it with the mouse.
- Remove a field from the report by clicking on its title and pressing Delete.
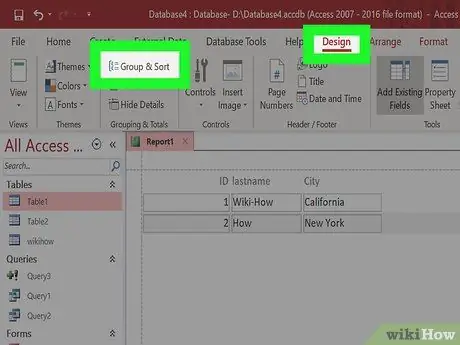
Step 5. Group your reports
Grouping allows you to quickly process information from reports, because related data is already organized. For example, you might want to group sales by region or by seller. Grouping allows you to do just that.
- Click the Design tab, and click "Group and Sort".
- Right-click anywhere in the field you want to group. Select "Group On" on the menu.
- A head will be created for the group. You can customize header titles to label groups.
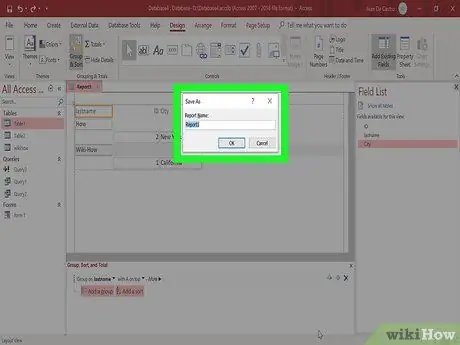
Step 6. Save and share the report
Once your report is complete, you can save and share or print it like any other document. Use reports to share performance reports with investors, contact information on workers, and more.
Tips
Microsoft Access opens in "Backstage View" mode, which provides menu options that allow you to open a database, create a new database, or access commands to edit your database
Warning
Some features in Access are not always available, depending on the type of database you are creating. For example, you cannot share a desktop database on the Web, and certain desktop features such as number of queries are not available on the Web database
== Source ==
- https://office.microsoft.com/en-us/access-help/introduction-to-queries-HA102749599.aspx?CTT=5&origin=HA102809525# _Toc355883441
- https://www.functionx.com/access/Lesson30.htm
- https://www.gcflearnfree.org/access2010/13
-
https://oit.wvu.edu/training/files/access2010reports.pdf






