- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 10:50.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
You can cut your finger while cooking or exercising. Finger injuries are a common medical injury and do not require emergency treatment to the hospital. However, if the cut on your finger is deep, you cannot stop the bleeding, or there is a foreign object in the wound (such as glass or metal shards), you should seek medical attention immediately.
Step
Part 1 of 2: Cleaning Wounds

Step 1. Wash your hands before touching the wound
Thus, you reduce the risk of exposing bacteria from your hands to the wound.
If disposable medical gloves are available, put them on your uninjured hand to prevent your wound from getting bacteria from your hands
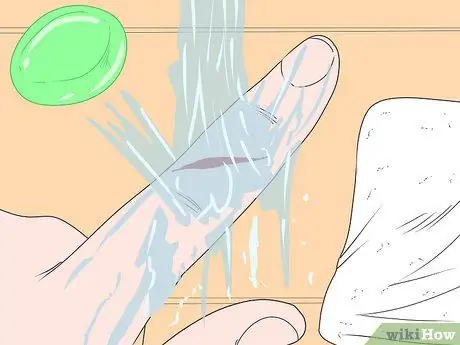
Step 2. Clean the wound
Use clean, running water to clean the wound. Prepare a clean cloth, wet it, then dip it in soapy water. Clean the area around the wound with the soapy cloth, but don't apply it to the wound as it can irritate it. When finished, dry with a clean, dry towel.
- If after washing there is still dust or debris in the wound, use tweezers to remove the debris. Before use, dip the tweezers in rubbing alcohol to sterilize them.
- You don't need to use hydrogen peroxide, rubbing alcohol, iodine, or an iodine-based cleanser to clean the wound, as these will irritate the injured skin.
- If the splinter remains or is difficult to remove, seek professional medical assistance at the nearest clinic or hospital.

Step 3. Watch for blood spurting or oozing out
If blood is spurting from the wound, it means that your artery is injured and needs immediate medical attention. Most likely, you won't be able to stop the bleeding. Apply pressure to the arterial incision with a clean cloth, towel, or sterile bandage and go to the emergency department immediately. Do not place a tourniquet (or a blood pressure device as it was attached before receiving the injection) on the wound.
If the blood is slowly flowing out, it means that your vein is injured. Venous sores will stop after about 10 minutes with proper treatment, and can usually be self-treated at home. As with any bleeding, apply pressure to the wound with a sterile bandage

Step 4. Look at the depth of the wound
Treatment of deep wounds that go through the skin and open wide, exposing your fat or muscle, requires stitches. If your wound is deep enough to require stitches, go to the emergency room at a clinic or hospital immediately. If your wound doesn't look too deep (just under the surface of the skin) and isn't bleeding too much, you can treat it yourself at home.
- If your wound is closed immediately (within a few hours) with stitches, it will reduce the appearance of the wound after it heals and reduce your risk of infection.
- Broadly speaking, if the wound is less than 3 cm long, less than 1/2 cm deep, and no deep structures (muscle, flesh, etc.) are disturbed, the wound is considered a minor wound and can be treated without stitches.

Step 5. Stop the bleeding
Minor bleeding usually stops bleeding on its own after a few minutes. If there is blood flowing through the wound, use a clean cloth or sterile bandage to apply pressure to the wound.
Place the cut above your head, higher than your heart. When raising your hand, make sure the bandage stays in place and absorbs blood

Step 6. Apply an antibiotic cream or liquid over the wound
Once the bleeding has stopped, keep the wound moist by applying a neosporin layer to the wound. Neosporin doesn't make your wound heal faster, but it can prevent infection and start your body's natural healing process.
Some people's skin can become inflamed from the use of neosporin. Avoid further use if your skin is red or inflamed

Step 7. Apply a bandage to the wound
Cover the wound with a bandage to keep it clean and prevent bad bacteria from entering the wound.
Use a waterproof cover or bandage to keep it in place while you shower. If the bandage you use is wet, take it off, dry it in the sun, reapply the cream you used with the bandage
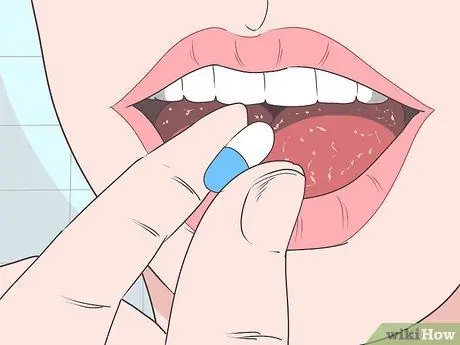
Step 8. Take an over-the-counter pain reliever
If your cut is painful, take ibuprofen to relieve the pain. Take according to the dose specified on the medicine package.
- Minor wounds should heal in a few days.
- Avoid taking aspirin as it can thin the blood and make your bleeding worse.
Part 2 of 2: Keeping Wounds Clean

Step 1. Change the bandage daily
You should also change the bandage if it gets dirty or wet.
Once your wound has healed sufficiently and a scab appears on the wound, you can safely remove the bandage. Your wound will heal faster if it is exposed to free air
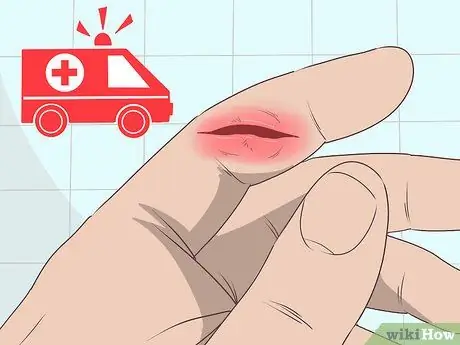
Step 2. Get medical help right away if your wound is swollen, red, filled with pus, or you have a fever
All of these are symptoms of infection. You need to consult a doctor if you experience these symptoms.
- If you are unable to move/use your hands or feel your hands are stiff, these are symptoms of a more serious infection and should be treated by a doctor immediately.
- Red streaks radiating from the wound are a sign of a severe infection and should be treated by a doctor immediately.
- If you are injured by an animal or human bite, you should immediately consult a doctor. Animal bites, especially wild animals such as raccoons or ferrets, can cause rabies. Pets and humans have bacteria in their mouths that can cause infection if they get into skin wounds.

Step 3. Ask for a tetanus shot if your wound is dirty or deep
After your wound has been cleaned and sutured by a doctor, ask for a tetanus shot to avoid infection.






