- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 10:50.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
Formally, the percentage error is the estimated value minus the exact value, and divided by the exact value per 100 cases (as a percentage). In essence, it lets you see how close the approximate value and the exact value are to the percentage of the exact value. These errors can be caused by miscalculations (tool or human error), or due to estimates used in calculations (eg rounding errors). Although it sounds complicated, the calculation formula is simple and easy to do.
Step
Part 1 of 2: Calculating the Value Part of the Equation
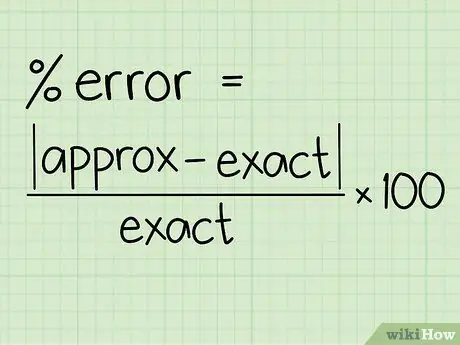
Step 1. Write down the percentage error formula
The formula for calculating the percentage error is quite simple: [(|Approximate Value - Exact Value|) / Exact Value] x 100. You will use this formula as a reference to enter the two values you need to know.
- The approximate value is the estimate, and the exact value is the original value.
- For example, if you guess there are 9 oranges in a plastic bag but there are actually 10, it means that 9 is the approximate value and 10 is the exact value.
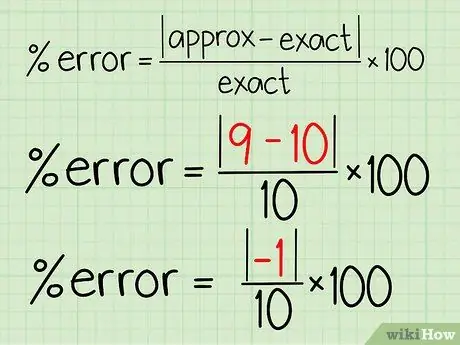
Step 2. Subtract the estimated value from the exact value
Using the orange example, you need to subtract 9 (approximate value) by 10 (exact value). In this case, the result is 9 - 10 = -1.
This difference is considered as the difference between the estimated and estimated values. This value indicates how far the expected results differ from what actually happened
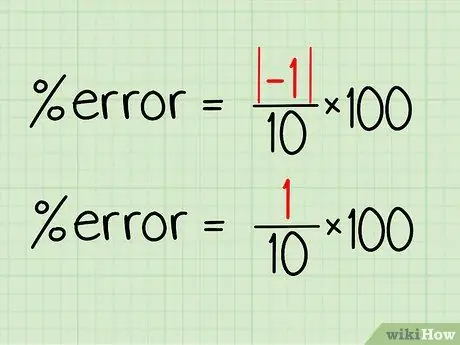
Step 3. Find the absolute value of the highest result
Since the formula uses the absolute value of the difference, the negative sign may be omitted. In this example, -1 would be just 1.
- Using the orange example, 9 - 10 = -1. The absolute value of -1, written as |-1|, is 1.
- If the result is positive, leave the numbers as they are. For example, 12 apples (approximate) - 10 apples (exact) = 2. The absolute value of 2 (|2|) is only 2.
- In statistics, looking for absolute values simply means that you don't care about the direction in which the forecast is missing (either too high or positive, or too low or negative). You just want to know how big the difference is between the estimated value and the exact value.

Step 4. Divide the result by the absolute exact value
Whether you're calculating with a calculator or manually, divide the top number by the absolute value of your exact variable. In this example, the exact value is already positive so you only need to divide 1 (from the previous step) by 10 (the exact value of oranges).
- For this example, 1/|10| = 1/10.
- In some questions, the exact value is a negative number from the start. In that case, ignore the negative symbol (that is, use the absolute value of the corresponding exact number).
Part 2 of 2: Completing Answers in Percentage Form
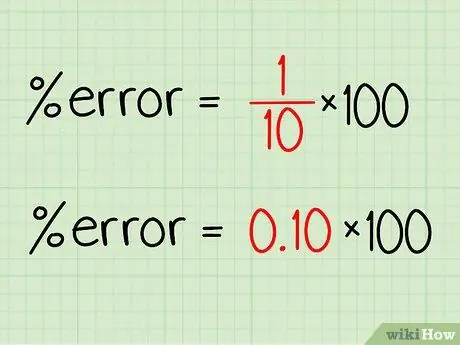
Step 1. Convert fractions to decimal numbers
To convert a fraction to a percentage, the easiest way is to start by converting it to a decimal number. In the previous example, 1/10 = 0, 1. The calculator will help you easily convert difficult numbers to decimals.
- If you can't use a calculator, you'll need to do long division to convert fractions to decimals. Usually, 4-5 digits after the comma are enough to be rounded.
- You must always divide numbers positive with numbers positive when converting it to a decimal number.
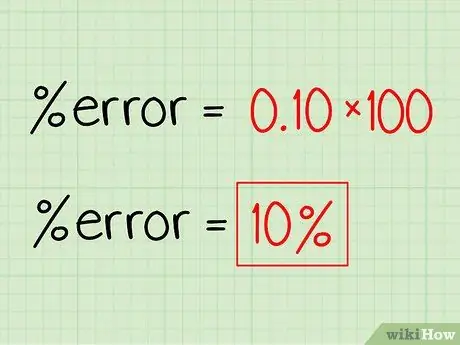
Step 2. Multiply the result by 100
Simply multiply the result, which in this example is 0, 1, by 100. This will convert your answer to a percentage. Just put a percentage symbol on the answer, and you're done.
In this example, 0.1 x 100 = 10. Apply the percentage symbol to get your percentage error, 10%

Step 3. Check your work to make sure your answer is correct
Typically, swapping signs (positive/negative) and division can cause minor errors in calculations. So, you should come back to check the correctness of the answer.
- In this example, we want to make sure that the estimate of 9 oranges is off by 10% of its original value, 10% (10% = 0.1) of 10 oranges is 1 (0, 1 x 10 = 1).
-
9 oranges +
Step 1. = 10 oranges. This ensures that the correct guess of 9 oranges misses by 1 orange from the original value of 10 oranges.
Tips
- Sometimes the approximate value is called the experimental value, and the exact value as the theoretical value. Make sure you use the correct values when comparing them to the original values.
- Uniquely, because you are taking the absolute value of the difference between the approximate and exact values, the order of operations in subtraction can be ignored. For example, |8 - 4| = 4 and |4 - 8| = |-4| = 4. The result value will be the same!






