- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2024-01-19 22:11.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
If you want to become a Java programmer, there are many new concepts to learn. There are classes, methods, exceptions, constructors, variables, and more; You can be overwhelmed learning it. So, you should learn them one by one. In this tutorial article, you will learn how to call a method in java.
Step
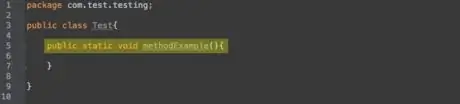
Step 1. Method equivalent to functions in programming languages like C, which helps in code reuse. Methods consist of a series of statements, and these methods can be called via other statements. When called, all statements that are part of the method will be executed. For example, consider this method:"
public static void methodExample() {}
. There is currently no code in it, but there are three keywords before the method name. There is
public
,
static
and
void
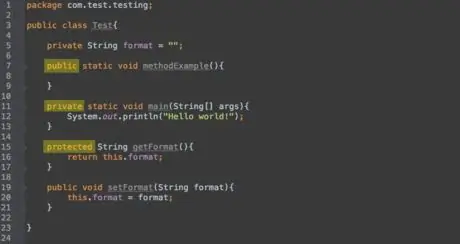
Step 2. Word
public
before the method name means that the method itself can be called from any place that includes another class, even from a different package (file) as long as you import that class.
There are other words that can replace
public
. The word is
protected
and
private
. If a method
protected
then only this class and its subclasses (classes that use this as the basis for compiling code) can call the method. A method
private
can only be called within that class. The last keyword is not really a word. The word is only used if you have no substitute
public
,
protected
or
private
. This word is called default, or package-private. This means that only classes in the same package can call the method.
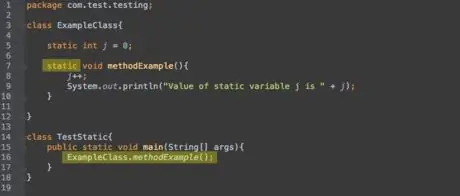
Step 3. Second keyword,
static
means that the method belongs to the class and is not an instance of the class (object).
Static methods must be called using the class name:"
ExampleClass.methodExample()
However, if the keyword
static
does not exist, methods can be called only through objects. For example, if class is called
ExampleObject
and has a constructor (to create an object), we can create a new object by typing
ExampleObject obj = new ExampleObject();
and call the method with"
obj.methodExample();
".
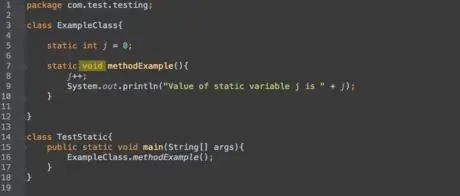
Step 4. Another word before the method name is
void
.
Say
void
means that the method returns nothing (returns nothing if you run the method). If you want a method to return something, just replace the word
void
with the data type (primitive or reference type) of the object (or primitive type) you want to generate. Just add
return
plus an object of that type somewhere before the end of the method code.
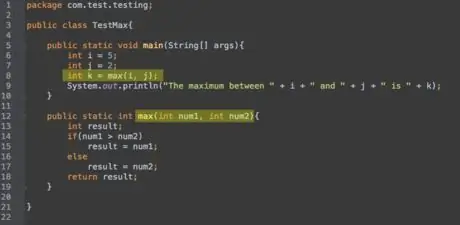
Step 5. When calling a method that returns something, you can use what was returned
For example, if
someMethod()
returns an integer, then you can set an integer to what is returned with"
int a = someMethod();
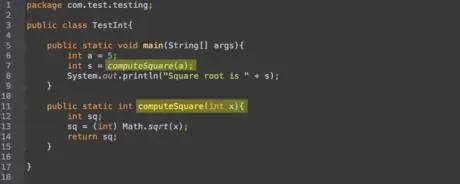
Step 6. Some methods require parameters
A method that takes an integer parameter would look like
someMethod(int a)
. When using a method like this, you must write the method name, then an integer in parentheses:
someMethod(5)
or
someMethod(n)
if
is an integer.
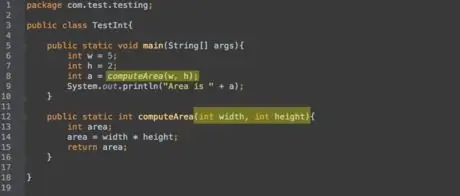
Step 7. Method can also have multiple parameters, just separate them with commas. If method
someMethod
requires two parameters,
int a
and
Object obj
will look like"
someMethod(int a, Object obj)
. To use this new method, you must call the method name followed by an integer and an Object in parentheses:
someMethod(4, thing)
with
thing
is a
Object
Tips
-
When you call a method that returns something, you can call another method based on what that method returns. For example we have a method named
getObject()
which produces an object. Well, in class
Object
no non-static method calls
toString
which produce
Object
in the form of
String
. So, if you want to get
String
it's from
Object
generated by
getObject()
in one line, just write"
String str = getObject().toString();
- ".






